obsidian
obsidian is a library for algorithmic process design and black-box optimization using AI-guided experiment design
pip install obsidian-apo
The obsidian library offers a set of modules for designing, executing, analyzing, and visualizing algorithmic process optimization (APO) using sample-efficient strategies such as Bayesian Optimization (BO). obsidian uses highly flexible models to build internal representations of the measured system in a way that can be explored for characterization and exploited for maximization based on uncertainty estimation and exploration strategies. obsidian supports batch experimentation (joint optimization and parallel evaluation) and is highly configurable for varying use cases, although the default specifications are encouraged.
We thank you for your patience and invite you to collaborate with us while obsidian is in beta!
Key Features#
End-User-Friendly: Designed to elevate the average process development scientist. No machine learning experience required.
Deployable using pre-built Dash application (
pip install obsidian-apo[app]). Each class is fully serializable, without third-party packages, to enable web-based API usage.Explainable and visualizable using SHAP analysis and interactive figures.
Flexible: Handles any input (numeric, discrete) and optionally input/output constraints, multiple outcomes, batch optimization, and a variety of novelty objective compositions. We know that experiment campaigns can have fluctuating objectives and resources, and obsidian is built to support that.
Purpose-Driven Development: Impactful features proposed, developed, maintained, and used by laboratory bench scientists. Revelantly designed for process development, optimization, and characterization.
How it Works: Algorithmic Optimization#
The workflow for algorithmic process optimization is an iterative workflow of the following steps:
Collect data
Fit a model to the data and estimate uncertainty across a design space
Search for new experiments and evaluate for objective and/or informational utility
Design experiments where utility is maximized
Repeat
The central object ob the obsidian library is the BayesianOptimizer, which can be optionally wrapped by a Campaign. A bayesian optimization has two key components that govern the optimization:
The surrogate model: A black-box model which is regressed to data and used for inference. Most often a Gaussian Process (
surrogate='GP').The acquisition function: A mathematical description of the quality of potential experiments, as it pertains to optimization. Most often Expected Improvement (
acquisition=['EI']).
Usage Example#
Specify Parameters & Initialize a Design#
from obsidian import Campaign, ParamSpace, Target
from obsidian.parameters import Param_Categorical, Param_Ordinal, Param_Continuous
params = [
Param_Continuous('Temperature', -10, 30),
Param_Continuous('Concentration', 10, 150),
Param_Continuous('Enzyme', 0.01, 0.30),
Param_Categorical('Variant', ['MRK001', 'MRK002', 'MRK003']),
Param_Ordinal('Stir Rate', ['Low', 'Medium', 'High']),
]
X_space = ParamSpace(params)
target = Target('Yield', aim='max')
campaign = Campaign(X_space, target)
X0 = campaign.designer.initialize(10, 'LHS', seed=0)
Temperature |
Concentration |
Enzyme |
Variant |
Stir Rate |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
8 |
17 |
0.1405 |
MRK001 |
Medium |
1 |
12 |
143 |
0.1695 |
MRK003 |
Medium |
2 |
4 |
101 |
0.2855 |
MRK002 |
High |
3 |
28 |
87 |
0.1115 |
MRK002 |
Low |
4 |
-4 |
115 |
0.2275 |
MRK001 |
Low |
5 |
-8 |
73 |
0.0825 |
MRK002 |
Medium |
6 |
20 |
129 |
0.0535 |
MRK001 |
High |
7 |
24 |
31 |
0.2565 |
MRK002 |
Medium |
8 |
16 |
59 |
0.1985 |
MRK003 |
High |
9 |
0 |
45 |
0.0245 |
MRK003 |
Low |
Collect Data and Fit the Optimizer#
campaign.add_data(Z0)
campaign.fit()
Suggest New Experiments#
campaign.suggest(m_batch=2)
Temperature |
Concentration |
Enzyme |
Variant |
Stir Rate |
Yield (pred) |
Yield lb |
Yield ub |
aq Method |
aq Value |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0 |
-10 |
10 |
0.0918096 |
MRK001 |
Medium |
112.497 |
102.558 |
122.436 |
EI |
0.848569 |
1 |
-10 |
150 |
0.0882423 |
MRK002 |
High |
89.8334 |
79.8589 |
99.8079 |
EI |
0.870511 |
Interpret Results#
from obsidian.plotting import surface_plot, optim_progress
surface_plot(campaign.optimizer, feature_ids=(0,2))
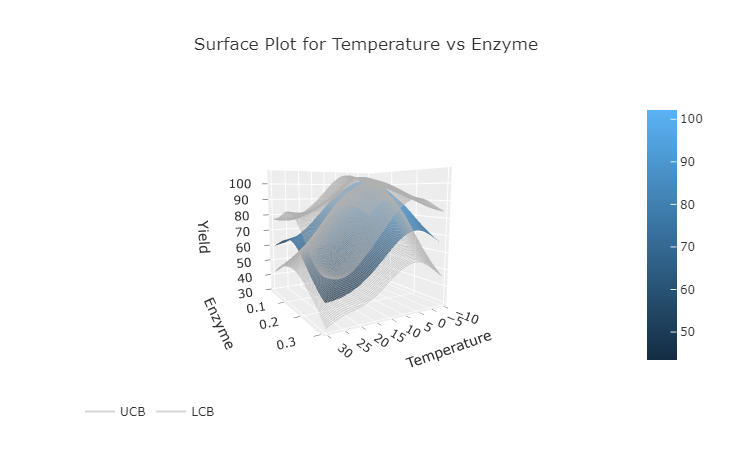
optim_progress(campaign)

from obsidian.campaign import Explainer
exp = Explainer(campaiagn)
exp.shap_explain()
exp.shap_summary()

exp.shap_pdp_ice(ind = 2, ice_color_var = 3)

Installation#
The latest obsidian release can be installed using pip:
pip install obsidian-apo
To install the required dependencies for running the Dash app:
pip install obsidian-apo[app]
Be sure to pip install in a newly created conda environment to avoid dependency conflicts.
Launching the App#
Clone this repository using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/MSDLLCpapers/obsidian.git
With obsidian-apo[app] installed on an activate Python environment, navigate to the new folder and simply run the folloiwng command:
python app.py
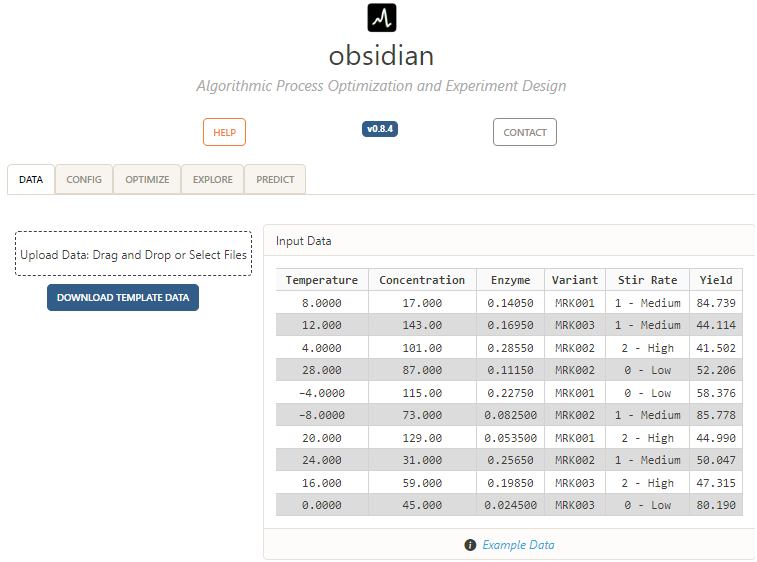
Contributing#
See CONTRIBUTING to learn more.
Developers#
Kevin Stone (Merck & Co., Inc.) kevin.stone@merck.com
Yuting Xu (Merck & Co., Inc.) yuting.xu@merck.com
Contributors#
Ajit Vikram (Merck & Co., Inc.)
Melodie Christensen (Merck & Co., Inc.)
Kobi Felton (Merck & Co., Inc.)
License#
obsidian is licensed by the GPLv3 license.





